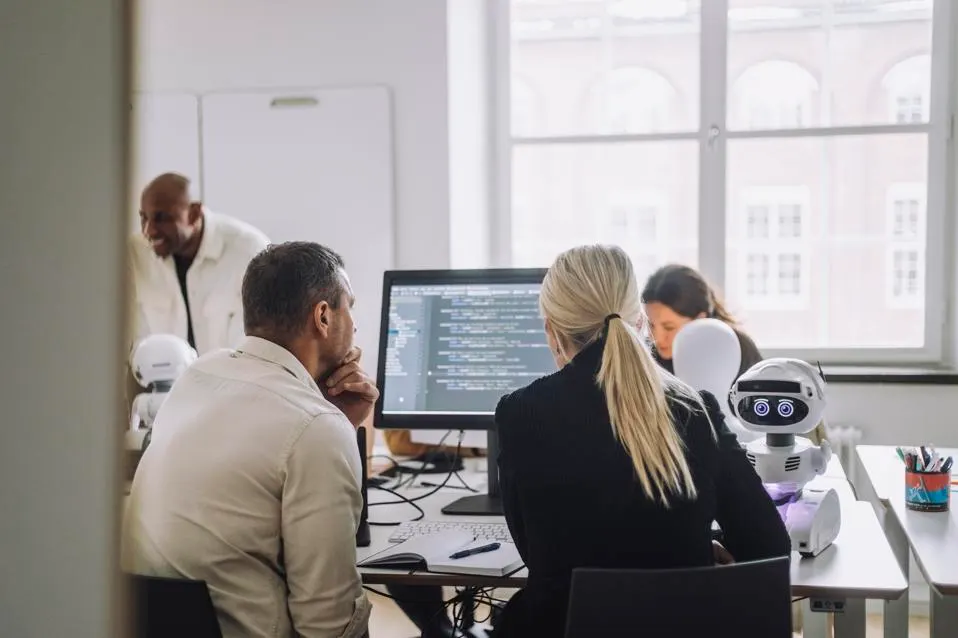
There's plenty of cynicism around the opportunities of generative AI—much of it warranted. (No, I don’t want a “poison bread sandwich,” thank you very much, Savey Meal bot.) However, I see two key events as creating the ideal conditions for AI to prompt a fundamental shift in how we can make technology more humane.
I know you’ve heard such promises before. In the early 2000s, the idea of “consumer-oriented” technology exploded—but its promise has so far been limited. Instead, people were forced to learn how to interact with the technology supposedly designed to serve them.
We were the ones who had to learn how to input and work around extensive corporate systems at work: Navigate a “Facebook,” learn how to rip songs from a CD onto iTunes and interact with files and photos in the cloud. As designers and engineers at the time, we forced everyone else to learn and adopt practices that fit what we built while consumer technology was just finding its footing.
Breaking The Mold: AI’s Role In Redefining Human-Machine Interaction
This sparked a boom of investment in ergonomics, human-centered design, interaction design and UX design—roles created because we didn’t make technology seamless in the first place. Case in point: the keyboard and mouse. For decades, the keyboard and mouse haven’t evolved much (despite causing a generation of carpal tunnel syndrome sufferers) because we’ve been taught to assume they’re the only way to input into a machine.
AI innovations like GenAI may finally change that with evolutions in text-to-speech/speech-to-text and the ability to generate 2,000 words of content based on a 15-word prompt. Much like the early days of the internet, although we are only now scratching the surface of how AI can trigger monumental improvements in human-centered experiences, there is endless potential.
A Spark To Ignite Technology Designed For All Of Us
Two major forces are at play that could transform how we interact with technology more naturally. First, the evolution of AI tools coincides with businesses worldwide investing in diversity, equity and inclusion practices. In the past, technology development has been skewed to suit the needs of specific demographics, namely wealthy white men in the western hemisphere.
Although there’s plenty of (accurate) criticism that datasets have huge gaps that create biases in their large language models (LLMs), I believe that we can change that using DEI principles and governance at the moment of technology conception. DEI, by its very nature, brings forward the priority and tools for equitable capacity, accessibility, empathy and direction for ensuring that whatever you’re creating approaches and interacts with people equitably—regardless of whether those people are differently abled, from different nationalities, use different languages or experience different cultural practices.
We witnessed the potential of weaving DEI into technology in the 2010s with Microsoft Kinect (today renamed to Azure Kinect), which I think was way ahead of its time in using technology like body and joint tracking so it could better interact with people of different races. Fast forward, and alternative inputs like voice, facial recognition and safety sensors are opening up much more natural and accessible forms of interaction.
A Co-Pilot For More Human-Centered Designers
The second factor I see opening up the potential for AI to permanently change how we interact with technology is the access to human-centered design talent and the recognition of the business world in the value of user experience. AI opens up a world for designers who no longer need to learn how to code. AI can get them most of the way toward their intended outcomes before having to engineer for scale.
That’s significant because AI, in the hands of human-centered designers, has the potential to introduce technology that interacts with people in a way that people work naturally—just like science fiction promised us.
And yet, I see many companies only looking at AI to deliver a short-term gain through head-count reductions and cost efficiencies. A few may look to grow their current feature set but will only prioritize a quick, small revenue bump and move on.
Bridging The Gap Between Science Fiction And Reality
Using AI to develop technology that interacts with humans more naturally and passively (versus forcing humans to interact inelegantly with technology) should result in some incredibly sticky products with excessively high adoption and low support and onboarding. The current terminal interface can cause an unnatural interaction between technology and people. GenAI as a voice interface could be one way we start making our sci-fi dreams come true. Yes, I’m talking Star Trek-level stuff.
Watch an episode, and you’ll see that Kirk never struggles with an interface. Spock isn’t adjusting to a huge learning curve. Sulu isn’t clumsily transitioning between devices. The technology is genuinely supportive and enabling for all different types of people. (Heck, in Star Trek for other species, too.)
But that kind of AI needs longer-term product experimentation to support the ideation and design efforts and the priority for ethics and governance. The companies making those investments today are the ones who will come out as the big winners.
Who’s going to make this happen? I wouldn’t count on the big technology firms. They’ve grown so large that they have to focus on massive and long-term onshore or offshore software development and data infrastructure engagements.
The exciting AI innovations will likely be done by smaller services and consulting teams in partnership with investors and companies looking for bigger returns over longer-term timelines. I think boutique professional services firms are ideally positioned because they can offer high collaboration and high-skilled talent to develop stickier, more human-centric AI innovation faster, delivering a long-term return over a medium-term duration.
We used to talk about leapfrogs in innovation. AI’s potential, combined with DEI and human-centered design talent, could be a real moonshot. The companies that take this leap can set a new standard for their digital products and services by completely transforming how technology interacts with people and redefining their category.